NOx Control
For NOx control, catalytic ceramic filter elements are manufactured with nanobits of SCR catalyst embedded in the walls.
The filter walls containing the catalyst are about ¾ inch (20 mm). Urea or ammonia (usually aqueous) is injected upstream of the filters. The catalyst embedded in the filters achieves NOx control with over 90 percent efficiency. NOx control, combined with particulate capture and SOx control, is a revolutionary advantage.
Note the lower operating temperature required for high NOx removal: 350°F to 400°F, compared with 650°F for conventional SCR. The catalytic filters also work well at the higher temperatures. NOx control at lower temperatures, such as can be achieved by boilers and other processes, is a revolutionary advantage.
Besides the need for high temperature, a common problem with traditional SCR is the catalyst becomes poisoned and ineffective, necessitating early replacement. Typical poisons are ordinary PM, metals, and HCl.
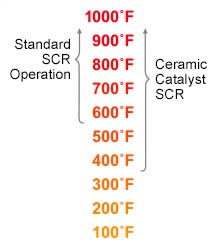
The lower operating temperature of the UltraCat Catalytic Filter Systems contrasts favorably with devices such as SCR used for NOx control.
Because our micronized catalyst is surrounded by filter material, it is almost 100% protected from blinding. When combined with acid gas removal using dry sorbent injection, other poisons like HCl, along with SO2, are removed at very high rates. In addition, the catalytic filter has a proprietary chemistry that results in a fraction of the conversion rate of SO2 to SO3 seen with traditional SCR catalysts. NOx control that extends the catalyst life to 5 years, 10 years, or beyond, is a revolutionary advantage.
The increased reactivity shown by the catalytic filters at lower temperatures results, in part, from their micronized form. The diffusion restriction is eliminated, unlike conventional big-block SCR where diffusion is a major restriction. The nano-catalyst is protected from blinding by particulate matter since it is embedded inside the filter. Ammonia slip is less than 5 ppmv, and generally less than 2 ppmv. NOx control that reaches high removal efficiency with minimum ammonia slip is a revolutionary advantage.
